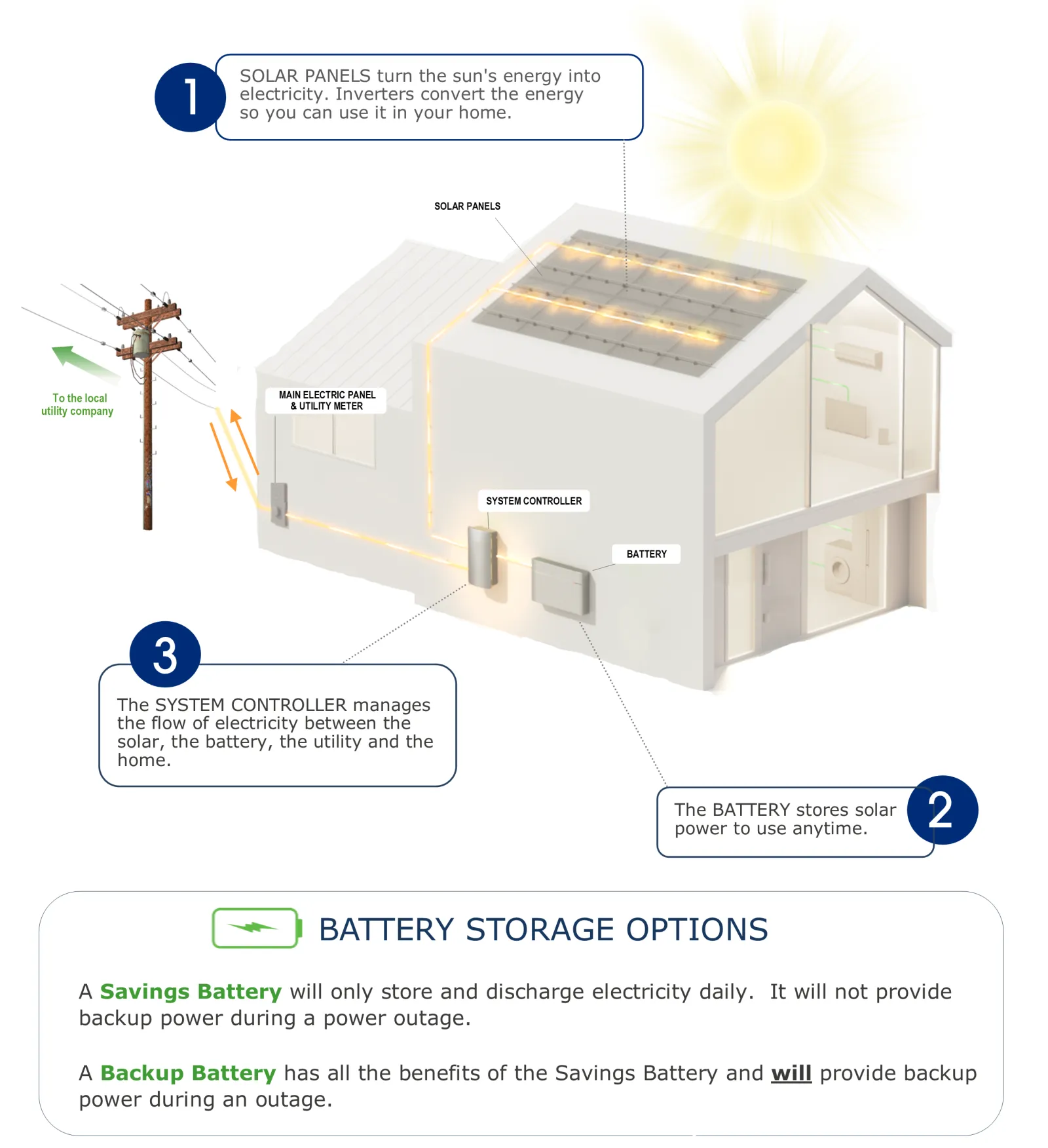
Solar Power & Battery Backup – How it Works
Solar Panels and Battery Backup — How Sunlight is Turned Into Electricity and Stored to Power Your Home
A solar photovoltaic (PV) system consists of one or more photovoltaic (PV) solar panels. One solar panel consists of about 36-72 photovoltaic solar cells. The cells convert the light into electricity. The solar panels are connected in a series called an array. Because PV Arrays are built with individual, linked solar panels, solar photovoltaic systems are exceptionally modular, which provides for easy transportation and rapid installation, and enables easy expansion if power requirements increase.
Solar systems that are grid-connected or "grid-tied" applications need an inverter, microinverters or power conditioner to convert the direct current (DC), generated by the solar panels, into alternating current (AC) for use in your home or business. Excess solar electricity generated and not used immediately is "sold" back to the utility for a credit to be used when sunlight is not available. This is called Net-Metering.
If a Home Solar Battery Backup System is added, the Battery stores excess solar power, rather than sending it back to the grid. This stored solar electricity can be used anytime; during a PG&E outage, during peak hours to reduce energy bills, or at night to avoid using grid power. There is also the option of a Savings Battery, which will only store and discharge electricity daily. It will not provide backup power during a power outage but is more affordable.
How PV (Photovoltaic) Solar Cells Work
The photovoltaic cell is the component responsible for converting light to electricity. When sunlight strikes a photovoltaic cell, part of the light particles (photons), which contain energy, is absorbed by the cell. By the absorption of a photon a (negative) electron is knocked loose from a silicon atom, and a positive "hole" remains. The freed electron and the positive hole together are neutral.
Therefore, in order to be able to generate electricity, the electron and the hole need to be separated from each other. A photovoltaic cell has an artificial junction layer, also called the p/n-layer. Now, the freed electronics cannot return to the positive charged holes. When the electric contacts on the front and rear are being connected through an external circuit, the freed electrons can only return to the positively charged holes by flowing through this external circuit, thus generating current. The electrical power that can be extracted from a photovoltaic cell is proportional to its area and to the intensity of the sunlight that hits the area, and is measured in watts (W).
The PV cells currently on the market convert an average of 12% to 15% of the sunlight that strikes them into electricity.
Solar Panel Orientation
Having a true south orientation of 180 degrees will typically produce the most amount of energy production per year. But many systems are installed in orientations besides true south, with only a small reduction in total output. Considerations on orientation include, site conditions, site shading issues, aesthetics, panel tilt and electrical rate schedules. If you plan to be on a Time-Of-Use (TOU) rate schedule, then a westerly facing system will produce the most energy within the "Peak" time period, where you accrue energy credits at the higher Peak rates.
These modifiers are used for the central California area and may be different for other areas of the country or different climatic circumstances.
The number one rule is to never design or install a solar electric system that faces in any portion of the 180 degree arc of the compass that faces north. When you need it the most it won't work. Needless to say, installing solar panels in the shade of a tree or building will also not be functional. The performance and therefore the return on investment (ROI) from a solar power system can be severely affected by shading-especially shading that occurs regularly due to an object that casts a shadow at the same time every day as the sun passes through the sky.
However, a newer technology using solar 'microinverters', allow solar panels to operate independently of each other. So if one module ends up in the shade, the others just keep on buzzing, resulting in much higher average system availability. That's especially great news for solar arrays with inconsistent shading profiles.
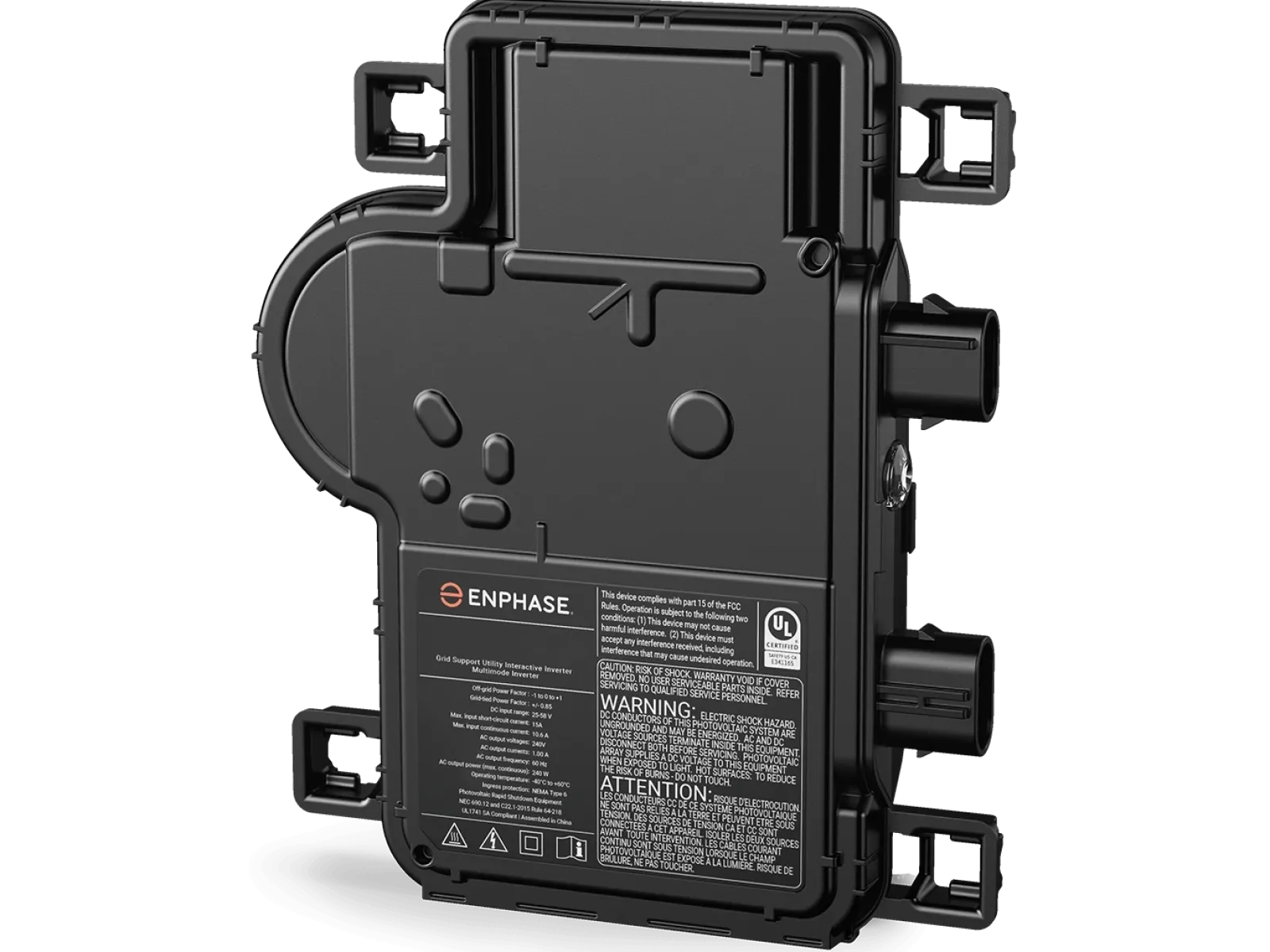

Microinverters
Solar panels turn the sun's energy into direct current (DC) electricity. Microinverters, An alternative to large, central inverters, beneath each solar module convert the DC to AC power to use in your home. With Enphase microinverters, each small micro-inverter is attached to each individual solar panel. These microinverters allow each panel to operate independently, leading to significant improvements in energy production, and flexibility of array design, especially when shading is an issue.
The microinverters also transmit information about how your system is performing through the Internet so that you and your solar professional can monitor your system.

How Net Billing Tariff Works for North Bay Solar
PG&E's new program, as of April 15, 2023, is called Net Billing Tariff, often referred to as NEM 3 and promotes the use of batteries in combination with solar. This shift not only helps homeowners lower their bills but assists PG&E in managing energy flow throughout the grid. This is especially important in California as heat waves become more common and utilities can't meet energy demands.
Battery storage enables you to optimize energy consumption patterns. You can draw from stored energy during expensive peak hours, minimizing your reliance on grid power which comes at higher rates during high-demand periods.
In the past, the program was called Net Energy Metering (NEM), which allowed solar panel owners to sell excess energy back to the grid, effectively reducing their utility bills.